Properties of metals


All pure metals (from a chemical point of view) are simple substance, that consist of atoms of one chemical element. In the periodic table metallic properties of elements increase from right to left. All pure metals (as one elements) are simple substances.
Properties of metals
There are physical and chemical properties of metals. In general, properties of metals are quite variety. There are metals alkaline, alkaline earth black, color, lanthanides (or rare earth metals - related to chemical properties of alkaline earth metals), actinoid (most of them are radioactive elements), and noble and platinum metals. In addition, certain metals have metallic and nonmetallic properties. Such metals are amphoteric (or transition).
Almost all metals have some common properties: a metallic luster, the structure of the crystal lattice, the ability in chemical reactions to show properties reductant and not to oxidize. In chemical reactions ions of dissolved metals form salts in the interaction with the acid, by interaction with water (depending on the activity of the metal) form alkali or base.
Why are shining metals

Atoms are contained in the crystal lattice of the metal. The electrons are moving around atoms and form "e-gas" what can free to move in different directions. This property explains the high electrical and thermal conductivities of metals.
Electronic gas reflects almost all of the light rays. That is why the metals so much shine and often have grey or white color. Communication between the individual layers of metal are small, allowing to move the layers under load in different directions (deformed metal).
So, pure gold is unique metal. With forging of pure gold can get foil with the thickness 0,002 mm! Such a thin piece of metal is semi-transparent and has a green tint if to see through it into the sunlight.
Electro physical property of metals
Electro physical property of metals is expressed in its conductivity. It is considered, that all metals have high conductivity, that is good conduct electric current! But it is not, and besides, it all depends on the temperature, at that is measured the current. Imagine a crystal lattice of metal, in that the current is passed through the movement of elec. That is the electrical conductivity also depends on, how easily the electrons can move between the points of the lattice. It can say, that the conductivity of the metal depends on the crystalline lattices and density of particles.
Particles in the lattice have vibrations, and these vibrations greater, than higher the temperature of the metal. Such vibrations significantly prevent the movement of electrons in a crystal lattice
Thus, the lower the temperature of the metal, the greater its ability to conduct current!
Hence the concept of superconductivity, that occurs in the metal at temperatures close to absolute zero! At absolute zero (-273 0C) oscillations of the particles in the lattice is completely fade!
Electro physical property of metals, that is associated with the current passage, is called temperature coefficient of electrical resistance!
Interesting fact that, for example, lead (Pb) and mercury (Hg) at the temperature a few degrees above absolute zero, almost completely disappears resistivity, there comes a condition of superconductivity.
Silver (Ag) has the high electrical conductivity,then copper (Cu), next is gold (Au) and next is aluminium (Al). High electrical conductivity of these metals is used in electrical engineering. Sometimes, to ensure chemical resistance and anticorrosion properties use gold (gold electrical contacts). It should be noted that the electrical conductivity of metals is much higher than the conductivity of non-metals. Here, for example, the carbon (C - graphite) or silicon (Si) has the conductivity is 1000 times less than, for example, mercury. In addition, the non-metals most of them are not conductors of electricity. But among non-metals are found semiconductors: germanium (Ge), silicon crystal and some oxides, phosphites (chemical compounds of metal with phosphorus) and sulfides (chemical compounds of metal and sulphur).
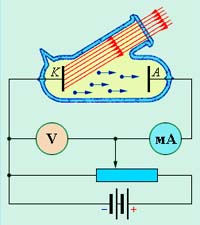
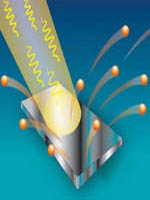
You probably know the phenomenon of photoelectric effect is a property of metals to give electrons under the action of temperature or light .
As for the thermal conductivity of metals, it can be estimated from the periodic table, - it distributes just like the electronegativity of metals. (Metals, located at the top left are most electronegativity, for example, the electronegativity of sodium equal -2,76). In its turn, metals have the thermal conductivity due to the presence of free electrons, that transport heat energy.