






Lead
Pure lead (Pb) - silver metal, heavy and fusible, having a bluish sheen. Lead - refers to low-melting metals. The melting point of lead is low and is only 327 0C (melts at home on a gas stove).
The lead has an amazing soft - in pure form this metal is easy to cut with a knife. Air lead tarnish, covered with a thin film of lead oxide PbO or basic lead carbonate Pb3(OH)2(CO3)2. At room temperature, the lead is inert to hydrochloric and sulfuric acids, as covered with a protective film of insoluble salts, but readily reacts with nitrogen, and the air - even with a weak acetic acid: 2Pb+4CH3COOH+O2=2Pb(CH3COO)2+2H2O. Resulting from this reaction, the acetate of lead is called sugar of lead for its sweet taste. However, do not test it yourself: all substances with lead, especially water-soluble, very poisonous. Strong poisoning occurs when ingested 0.3 g of lead compounds.
Zinc
Zinc (Zn) is a silvery white metal (melting point=420 0C, boiling point=906 0C), brittle at room temperature. When stored on the air, it acquires a light bluish tinge, covered with a thin film of zinc oxide ZnO or basic carbonate 2ZnCO3*Zn(OH)2 protects it from further oxidation. Zinc coated roofing iron. Note the rusted bars that were not coated. Even if the zinc coating is damaged, the iron still does not begin to rust until rusted all the zinc coating. The zinc is coating iron to protect it from rust. From galvanized iron made sheets, downspouts, buckets and many other products.
Zinc oxide ZnO (melting point=1975 0C) is used as a filler to give a transparent to white plastic, and mixed with linseed oil as white paint (zinc white). White powder of zinc sulfide ZnS, in that the Zn atoms are substituted on Cd and S on Se, under action of a stream of electrons radiates visible light - a thin layer of this substance was applied to the television screens, x-ray tube.
In the adult human body contains approximately 2.3 g of zinc, which is part of more than 40 enzymes that regulate carbohydrate and energy metabolism in the cells.
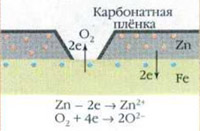
Zinc more active of iron and gives him a certain amount of electrons, and surface of iron charged negatively. Electrons are transferred to oxygen with the surface of the iron, originally belonged to the zinc. So the zinc is destroyed itself, protects the iron. Compare other metals in its ability to restore and recover you can reading number the stress of metals.
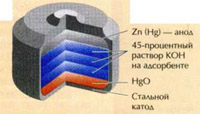
Chemical reaction, based on the ability of zinc to displace mercury from its compounds included in the mercury-zinc galvanic element. It takes the following process:
Zn+HgO=Hg+ZnO.
Mercury-zinc elements have not equal in terms of reliability, voltage stability and the number of "stored" electricity per unit mass. They are ideal for use in any places.
However, mercury is more than half of their mass. After the batteries are overage, there is the problem of their utilization. If you just throw these items in a landfill, the air around is poisoned. Why in the world there is a growing campaign against the use of mercury-zinc elements. In particular, to the public they no longer do. And on batteries, which are sold in stores, you can read: "Mercury 0%" or "Mercury free," meaning "no mercury".
Brass - copper-zinc alloys (containing from 4 to 50% Zn) - much stronger and cheaper than copper, more resistant to oxidation.
Alloys based on zinc have good casting qualities. For example, it is easy to cast nut with thread. (For steel, this possibility remains a distant dream.) Therefore, these alloys are actively used for casting of products with a very thin surface relief, such as typographic fonts.