Alkali
Base
Hydroxide

AlkaliBaseHydroxide |
 |
 quicklime 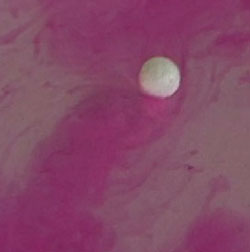 Dissolving an alkali metal in water with the changes of indicator's color to bright red
Solid grease.liquid grease. Grease properties
Alcohols. Properties of alcohols Resin. Phenol-formaldehyde resin
 The iron hydroxide 3 valence |
Bases are electrolytes with hydroxide-ions in solutions (anions - ions, which have a negative charge, in this case is ions of OH- ). The names of the bases consist of three parts: the words hydroxide, with added the name of the metal. For example, copper hydroxide (Cu(OH)2). For some bases can use the old names, such as sodium hydroxide (NaOH) - caustic soda. Sodium hydroxide, caustic soda are all one substance, whose chemical formula is NaOH. Anhydrous sodium hydroxide is a white crystalline substance. The solution is a transparent liquid, on the form like a water. When you use it - be careful! Caustic soda burns the skin! To classification of bases included their ability to dissolve in water. Some properties of bases depend on solubility in water. So, bases, soluble in water, is called the alkali. These include sodium hydroxide (NaOH), potassium hydroxide (KOH), lithium hydroxide (LiOH), sometimes to their number added calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2)), but in reality it is substance poorly soluble in whate and has white color (slaked lime). Getting basesFor getting base and alkali are used various ways. For getting alkali you can use the chemical reaction of the metal with water. Such reactions occur with very high heat and may ignite (hydrogen can ignite in the reaction).2Na + 2H2O -> 2NaOH + H2 CaO + H2O -> Ca(OH)2 But in industry, these methods have not found practical value, of course in addition to getting a calcium hydroxide Ca(OH)2. Getting sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide do due use of electric current. When electrolysis aqueous solution of sodium chloride or potassium hydrogen forms on the cathode and chlorine forms on the anode. In solution, where electrolysis, accumulates an alkali! KCl + 2H2O ->2KOH + H2 + Cl2 (this reaction goes when electric current is passed through the solution) Insoluble bases are got with alkali from solutions of the corresponding salts. CuSO4 + 2NaOH -> Cu(OH)2 + Na2SO4 Properties of basesAlkali resistant to heat. For example, sodium hydroxide can be melted and the melt bring to a boil, it will not decompose.Alkali easily react with acids to form salt and water. This reaction is called - neutralization reaction KOH + HCl -> KCl + H2O Alkali react with acidic oxides, form salt and water. 2NaOH + CO2 -> Na2CO3 + H2O
Insoluble bases, in contrast to alkali, non-persistent substances. Some of them, for example, copper hydroxide, is decomposed then heat, 2Na+2H2O=2NaOH+H2 All alkali metals do same as sodium. If add to the water phenolphthalein indicator before the beginning of the reaction and then place alkali metal in the water, so it will slide on the water, leaving a bright pink mark formed alkali (alkali paint the phenolphthalein in pink) Гидроксид железаIron hydroxide is the base. Iron forms two different bases, depending on the degree of oxidation: hydroxide of iron, where iron can have a valency (II) - Fe(OH)2, and (III) - Fe(OH)3.As the bases, formed by most metals, both hydroxides of iron are not soluble in water. Iron hydroxide (II) - white gelatinous substance (precipitate in solution), that has strong reducing properties. In addition, iron hydroxide (II) is not stable. If to a solution of iron hydroxide (II) add a little alkali, then drop off the green precipitate, which quickly darkens and turns into a brown precipitate of iron(III). Iron hydroxide (III) has amphoteric properties, but the acidic properties it has significantly weaker. Get the iron hydroxide you can (III) with reaction between the iron salt and alkali. For example Fe2(SO4)3 + 6 NaOH -> 3 Na2SO4 +2 Fe(OH)3
|
Alloys of pure metals
Indicator pH. Color of indicator Crystal growing. How to grow crystal Color glass. The crystal. Quartz glass Complex substances. Water hardness Cooling mixture. Endothermic reaction Length unit. Units of volume. Unit weight. Units square Color of gold. Alloys of gold. Stamp of gold Food additives, conserving agents The density of substances (materials)
|